For a Concave Mirror, an object can be placed at any position so that image is created at different - different positions. We can find image position, its nature, and its size using Ray Diagrams.
Case - 1
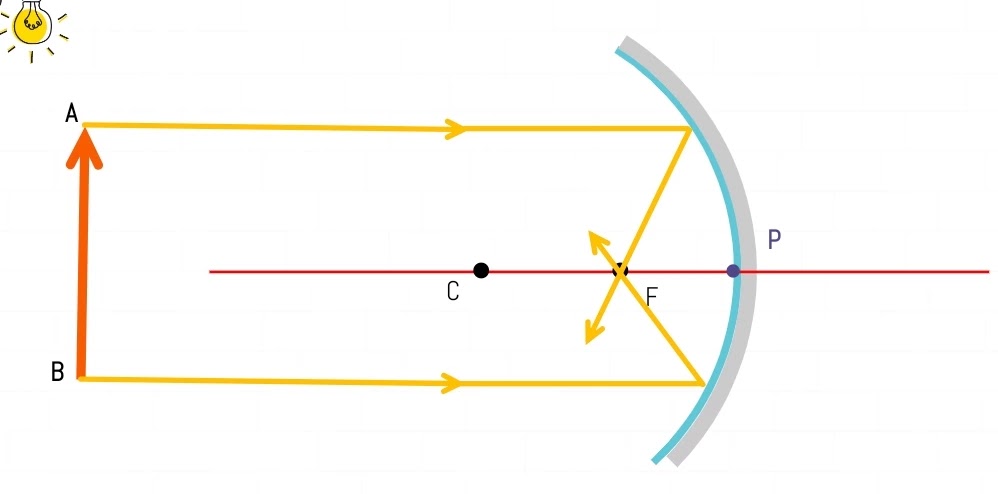
Object(AB) is placed at infinity
Here as shown in figure two light rays parallel to Principal Axis pass through Focus after reflection. So the image is formed on the Focus of the mirror.
Result:-
| Object Position | At Infinity |
| Image Position | At Focus (F) |
| Nature of Image | Real and Inverted |
| Image Size | Point Sized |
Case - 2
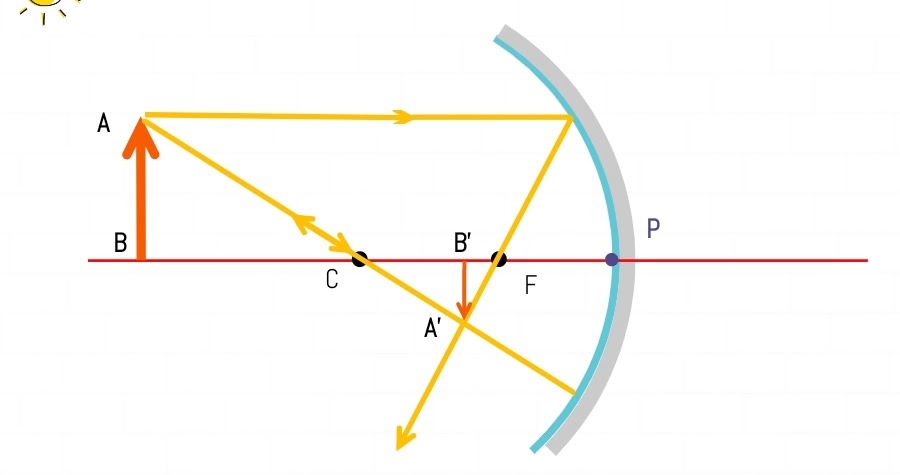
An object placed beyond the Center of Curvature (C)
Result:-
| Object Position | Beyond Center of Curvature (C) |
| Image Position | Between Focus (F) and Center of Curvature (C) |
| Nature of image | Real and Inverted |
| Image Size | Smaller |
Case - 3
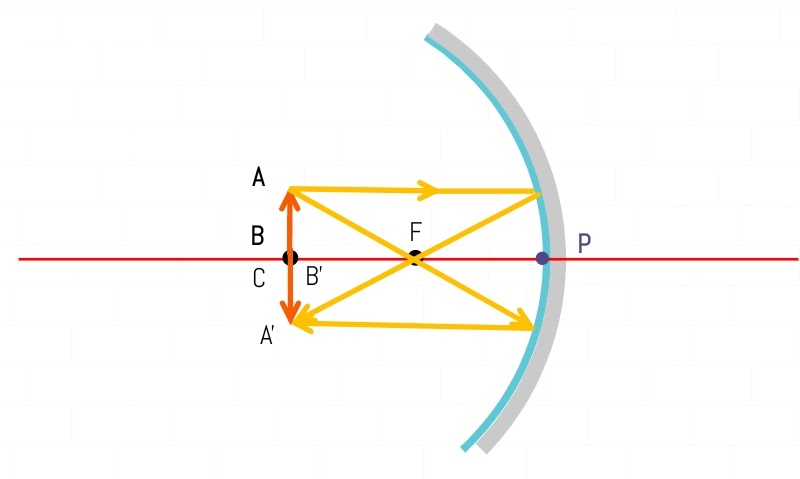
An object placed at the Center of Curvature (C)
Result:-
| Object Position | At Center of Curvature (C) |
| Image Position | At Center of Curvature (C) |
| Nature of image | Real and Inverted |
| Image Size | Same |
Case - 4
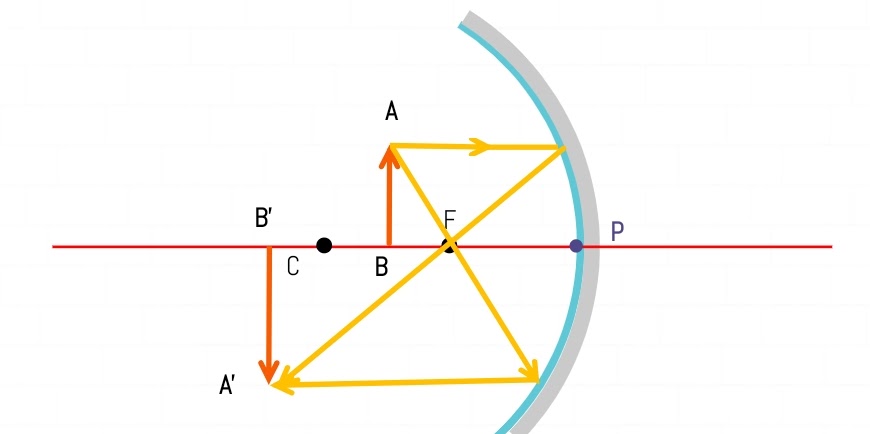
An object placed between the Center of Curvature (C) and Focus (F)
Result:-
| Object Position | Between Center of Curvature (C) and Focus (F) |
| Image Position | Beyond Center of Curvature (C) |
| Nature of image | Real and Inverted |
| Image Size | Enlarged |
Case - 5
An object placed at Focus (F)
Result:-
| Object Position | At Focus (F) |
| Image Position | At Infinity |
| Nature of image | Real and Inverted |
| Image Size | Highly Enlarged |
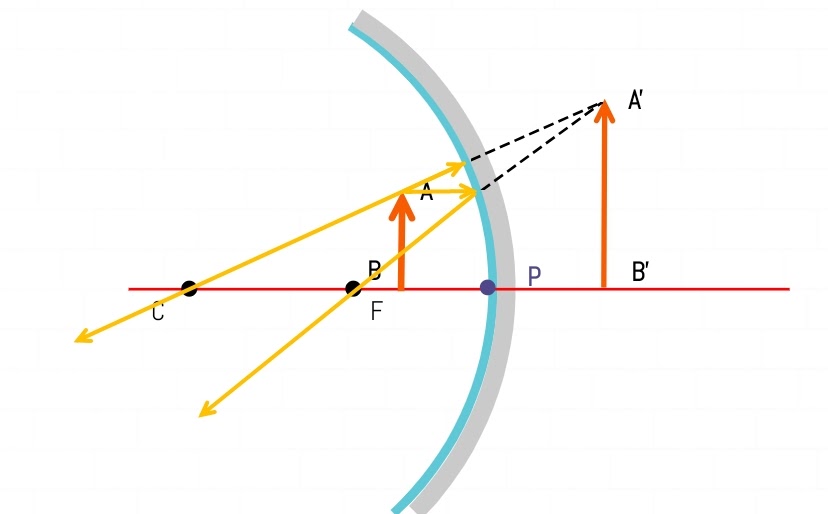
Case - 6
An object placed between Focus (F) and Pole (P)
Result:-
| Object Position | Between Focus (F) and Pole (P) |
| Image Position | Behind Mirror |
| Nature of image | Virtual and Erect |
| Image Size | Enlarged
|
Let us Summarise it all
| Object Position | Image Position | Nature of Image | Image Size |
|---|
| Infinity | Focus (F) | Real and Inverted | Point Sized |
| Beyond C | Between F and C | Real and Inverted | Smaller |
| At C | At C | Real and Inverted | Same |
| Between F and C | Beyond C | Real and Inverted | Enlarged |
| At F | At Infinity | Real and Inverted | Highly Enlarged |
| Between F and P | Behind Mirror | Virtual and Erect | Enlarged |
Uses of Concave Mirror
- It's used in the torchlight, searchlight, vehicle headlights to get a powerful parallel beam of light.
- It's used by dentists to see a large image of teeth of patients.
- It's used in a solar furnace as it helps to concentrate rays of sunlight at one point. It develops heat energy and later used for cooking or some other purpose as needed.
- It's used in a shaving mirror to see a large image of our face.